Table of Contents
Brain Information Flow Diagram (BIF)
WBAI proposes the Brain Information Flow Diagram (BIF) as a format for describing and sharing the whole brain architecture (cf. information flow diagram).
See also Brain Reference Architecture (BRA)
Overview
BIF is composed of Circuits and Connections between them.
A Circuit corresponds to a population of neurons, an organ in the brain such as the hippocampus, or a circuit consisting of brain organs, to perform a certain function.
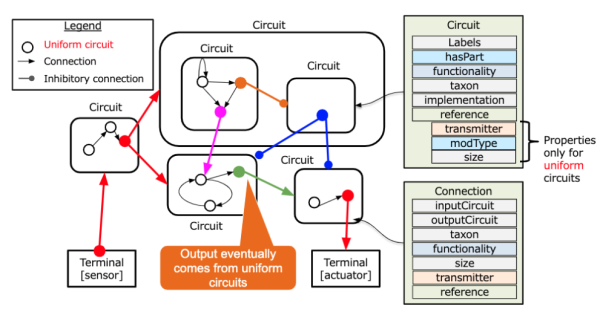
The BIF Ontology
BIF elements are defined by an ontology with the following classes and properties.
Circuits and Connections are normally defined as classes rather than instances.
(Click here for the OWL format file of the BIF ontology.)
Circuit
A collection of one or more brain regions or organs with the following properties.
- names: name list
- hasPart: Circuits within
- functionality: description of functions
- reference: reference list
- implementation: URLs (pointers to implementation)
- uniform: truth value (true iff it has no sub-Circuit and unique output)
- taxon : animal species (option)
UniformCircuit
A subclass of Circuit whose instance has unique output and no sub-Circuit
- uniform: True
They have the following properties in addition to the properties of Circuit.
- size: natural number (such as the number of neurons)
- transmitter: neurotransmitter
- modType: Excitatory, Inhibitory, Modulatory
Connection
Connections between Circuits with the following properties.
- inputCircuit: a Circuit
- outputCircuit: a Circuit
- transmitter: neurotransmitter
- functionality: description of function/semantics
- reference: reference list
- size: natural number (such as the number of axons)
- taxon: animal species
NeuroTransmitter
Neurotransmitter: e.g., dopamine
Preparing BIF data
Please refer to the BIF data preparation manual.
