Introduction
transformers and diffusion models, or generative AI or foundational models. They can be said to be non-brain-morphic AI, because they are not faithful to the brain, at least at the architectural level. It is still uncertain whether non-brain-morphic AI technologies will reach artificial general intelligence (AGI). However, with the remarkable spread of large-scale language models including ChatGPT in 2023, the possibility of AGI by non-brain-morphic AI has been attracting worldwide attention, and the possibility of its realization by 2027-2030 is becoming impossible to ignore.
On the other hand, we have long advocated the whole brain architecture approach that refers to the brain architecture in order to construct human-brain-morphic AGI. The approach has the following two advantages
- Accelerated development: Referencing brain structure and function has the advantage of limiting the design space for AGI models to accelerate development. It directly facilitates the development of human-brain-morphic AGI and consequently accelerates the overall development of AGI.
- Affinity with human beings: Modeling AGI that is similar to humans in internal structure has the advantage of improving intrinsic interpretability and building AGI that is easier for humans to understand and trust. It can also lead to medical applications, such as modeling mental illness, and a basis for mind uploading.
Recent changes in the technological landscape have also had an impact on the two advantages.
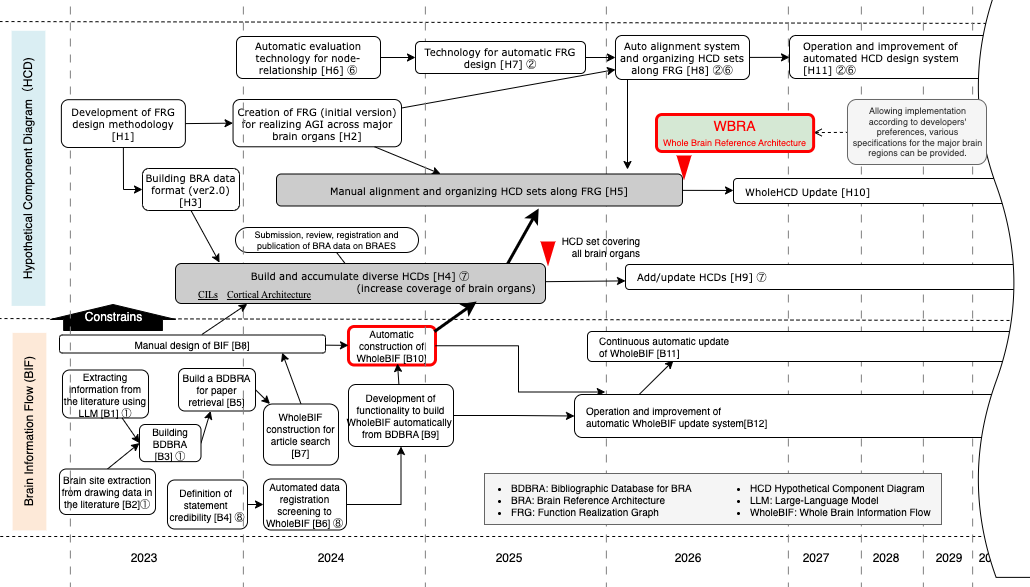
Figure 1: Whole Brain Architecture Technology Roadmap
WBRA (Whole Brain Reference Architecture) serves as
specifications of human-brain-morphic AGI.
With regard to the acceleration of development, we have announced a development roadmap (Figure 1) that reflects the latest neuroscience findings and aims for the release of a system capable of semi-automatically generating specifications for human-brain-morphic AGI by 2027. The feasibility of the system is being made possible by the assumption that rapid advances in LLM technology will enable much of the development process to be automated. In addition, it could deal with unpredictable AGI completion timelines, by building a system that generates specifications rather than aiming to produce specifications at a certain point in time.
On the other hand, with regard to the affinity with human beings, the positioning of AI in terms of the risks posed by its rapid progress is becoming increasingly important. There is a possibility that if AGI emerges at some point, it will reach a superintelligence that surpasses all humans within a few months or so, since AI itself can recursively improve itself. There is concern that this superintelligence could have catastrophic effects on humanity. For this reason, there has been a lot of research toward the realization of “AI alignment,” which aims, among other things, to adjust AI so that it behaves in accordance with humans’ intentions and values.
Against this backdrop, human-brain-morphic AGI has affinity with human beings and brain-based interpretability. Such characteristics make human-brain-morphic AGI understandable and trustworthy to humans. Furthermore, human-brain-morphic AGI can serve as a bridge between humans and superintelligence by enabling rapid interaction with superintelligence. In particular, brain-based interpretability refers to the property of being able to understand AGI computational processes (including conscious and unconscious aspects) at a cognitive level in terms of corresponding human neural activity (Figure 2). This is expected to make explicit the internal states (beliefs, intentions, pleasure, suffering, etc.) that underlie AI decisions and actions. The brain-based interpretability of the AGI system increases the likelihood that humans will discover and address inconvenient intentions and deceptions when they are formed.
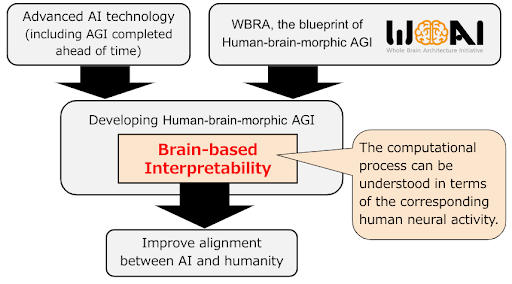
Figure 2: Brain-based Interpretability
Whatever form of AGI is completed, it will also make building brain-morphic AGI easier. Brain-morphic AGI will occupy an important position in the overall development of AGI because of its unique advantages such as affinity with humans and interpretability. Therefore, developing the technological conditions necessary for the construction of brain-morphic AGI while taking into account the realization of AGI will provide a beneficial option for humankind. In other words, WBAI can provide value to society through the advantages inherent in human-brain-morphic AGI. As rapid advances in AI technology increase risks, including human survival, WBAI, the NPO, aims to contribute to the reduction of such risks by developing technology to semi-automatically create specifications for highly interpretable human-brain-morphic AGI.
The following is the policy for our education and R&D businesses for the fiscal year 2024.
Education Business
The objective of the education business is to develop and increase the number of interdisciplinary personnel with different expertise in AI/ML, neuroscience, and cognitive science necessary for R&D in the WBA approach over the long-term. We continue our regular activities of holding seminars and an annual symposium to raise public interest.
We shall promote the progress of our organization by participating in and cooperating with external academic events and by cooperating and exchanging information with external academic organizations. In addition, we will also foster and involve human resources through cooperation with external researchers, engineers, and groups.
We shall invite applications to the WBAI Incentive Award to recognize those who have made significant contributions to the promotion of brain-inspired AGI technology, thereby invigorating the community. We also continue our activities to promote the human-brain-morphic AGI that we promote to develop to be aligned with humanity.
Research and Development Business
The R&D business aims to accelerate democratic AGI research via the WBA approach on open platforms by taking advantage of our being a non-profit organization to avoid competition with other research organizations in AGI research, and by promoting Brain Reference Architecture (BRA)-driven development. The following activities will be carried out for FY2024.
Table: WBA R&D Category List
| Large Category | Medium Category | Description |
| Methodology | BRA data management system | Developing methodologies such as BRA data, submission review flow, BRAES, review tools, etc. |
| Methodology | BRA Visualization | Methodology for BRA data visualization |
| Methodology | HCD design | Methodology of HCD design |
| Methodology | BRA in general | Methodology of BRA-driven development |
| Operation | BRA data management system | Operation of BRA data, submission review flow, BRAES, review tools, etc. (including manual maintenance, version updates, etc.) |
| Operation | BRA Visualization | Operation of BRA data visualization tool and optimization of layout and display items |
| Operation | WholeBIF Management | Screening and registration of items to be added to WholeBIF (and BDBRA) |
| Operation | Data update | Data version control |
| Design | BRA data management system | Design of BRA data, submission review flow, BRAES, review tools, etc. |
| Design | BIF construction | BIF construction and related work |
| Design | HCD design | HCD design and related work |
| Design | WholeBIF construction | Construction of BIF data for the entire brain |
| Design | WholeHCD construction | HCD integration for the entire brain |
| Evaluation | BIF credibility assessment | BIF credibility assessment |
| Evaluation | HCD evaluation | HCD functionality/structural consistency evaluation and review flow/automatic review |
| Evaluation | Fidelity evaluation | Implementation evaluation (including abnormal systems), activity reproducibility evaluation, and functional evaluation |
| Evaluation | Abnormal system evaluation | Assessment of performance variation (human or animal dysfunction) |
| Evaluation | Activity reproducibility evaluation | Comparative evaluation of software behavior and neural activity obtained in experiments |
| Evaluation | Structural fidelity evaluation | Structural similarity evaluation of implemented code |
| Evaluation | Preparation of execution environment | Preparation of task execution/test environments for brain-inspired software |
| Implementation | BRA data management system | Implementation of BRA data, submission review flow, BRAES, review tools, etc. |
| Implementation | Development environment preparation | Building software platforms (BriCA etc.) |
| Implementation | Architecture implementation | Architectural implementation in a software framework with reference to HCD (in formats that allow structural fidelity evaluation) |
| Implementation | Component implementation | Software component implementation referring to HCD’s circuit process descriptions (in formats that allow activity reproducibility evaluation) |
| Implementation | Environment platform implementation | Building execution environment platforms (with OpenAI Gym, etc.) |
| Non-BRA | Validating new features | Implementation for exploring unknown computational mechanisms (for specific tasks that can be solved by animals including humans) |
| Non-BRA | Designing new features | Design of unknown computational mechanisms (for specific tasks that can be solved by animals including humans) |
| Non-BRA | Human resource development | Educational implementation to develop engineers for the implementation process |
| Non-BRA | AI alignment | Activities aiming for alignment between AI and humanity |
The following sections describe in detail the BIF and HCD construction activities that are the central part of BRA-driven development, as shown in the partial roadmap (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Planned activities in the WBA technology roadmap for FY2024
BIF Construction
As part of our BIF construction efforts, we have set a goal to build WholeBIF fully automatically by the end of 2024. Toward this goal, we will proceed with BIF construction activities in the following steps.
First, in the first half of the year, we plan to complete a paper retrieval system using BDBRA [B5], and then use this system to build and complete a WholeBIF specialized for paper retrieval [B7]. In addition, work on defining the reliability of information from the literature [B4] will be completed in the first half of the project, and on that basis a screening process for automatic data entry into WholeBIF will be built [B6]. Using this process [B6], we will begin developing the functionality to automatically build WholeBIF from BDBRA [B9].
By the end of the year, we will use the results of this auto-build functionality [B9] to move fully into the automated construction of WholeBIF [B10], which will effectively eliminate the need for manual design [B8] for WholeBIF after 2025.
HCD Construction
With the goal of realizing WBRA in 2026, the following activities are planned to be promoted in the HCD (Human-Centered Design) construction in 2024.
We aim to complete the BRA data format (version 2.0) [H3], which has been underway since 2023 to support the FRG (Functional Realization Graph), and use this to promote the construction and accumulation of diverse HCDs [H4].
We will also work on the first version of the FRG [H2] for AGI across major brain organs, and use the results to promote the manual organization and assembly of HCD sets [H5] in line with the FRG.
By the end of 2024, we plan to complete the automatic evaluation of node relationships [H6], which will lead to the development of automatic FRG design technology [H7] in 2025.
Building Open R&D Communities
Activities to develop software and other research infrastructures to support research to realize the WBA approach, and activities to promote research using these infrastructures in collaboration and cooperation with other organizations will also be continued.
We promote the BIF construction to accumulate anatomical findings and the assignment of functional hypotheses on BIF using the SCID method [Yamakawa 2021] for the development of brain-morphic software. We will also promote the development of technology to evaluate the neuroscientific validity of brain-morphic AGI.
In 2024 we will hold the First International Whole Brain Architecture Workshop as part of the promotion of such development.
Working Toward a World with AI Aligned with Humanity
Taking advantage of the human-brain-morphic AGI built with the WBA approach’s high affinity for humans, we are facilitating the move toward a world with AI aligned with humankind.
One focus is on the development of applications that require interaction with humans. We have already made progress in the study of affective interaction, combining the amygdala mechanism of emotion with LLM, and we plan to continue to promote it.
We are also exploring the possibility of human-brain-morphic AGI with brain-based interpretability to bridge humanity and superintelligence and mitigate the negative impact of superintelligence on humanity. To this end, we will collaborate with organizations related to AI alignment as needed.
Budget for the Fiscal Year
The planned income is approximately 0.54 million yen, mostly from membership fees (the membership fees were 0.70 million yen in FY2022). The total of the planned income for the current fiscal year and the 7.37 million yen carried over from the previous fiscal year is approximately 7.91 million yen.
Expenditures will be approximately 1.63 million yen in total, including approximately 0.81 million yen for administrative expenses and approximately 0.82 million yen for operating expenses, including prizes and expenses for events and communication (in relation to the planned income for the current fiscal year, there will be a deficit of 1.09 million yen). To note, in the FY2023 budget, we planned to spend about 1.89 million yen in total, including about 0.81 million yen for administrative expenses and about 1.08 million yen for operating expenses.
Conclusion
As mentioned in the introduction, current advanced AI technologies are developed as non-brain-morphic AI without reference to the brain. In contrast, we continuously advocate a whole brain architecture approach to build human-brain -morphic AGI. This approach has two advantages: it accelerates AGI development and improves affinity with human beings.
In particular, “brain-based interpretability” with brain-morphic AGI is beginning to take on new importance today, when there is strong concern about the risk of advanced AI that could reach superintelligence. As design information for the human brain-morphic AGI, we aim to build the Whole Brain Reference Architecture (WBRA), which makes references to the structure and function of the human brain and provides software design information for implementing brain-morphic AGI. No matter how the first AGI is completed, WBRA will facilitate the building of brain-morphic AGIs as needed.
In recent years, some have suggested that AGI may be completed around 2027. In light of this technological outlook, WBAI has also created a roadmap that aims to complete a system capable of semi-automatically generating WBRAs by 2027.
At present, WBAI is the only organization aiming to provide software design information for brain-morphic AGI that can fully reproduce human cognitive functions. As part of this effort to achieve brain-morphic AGI, we adjusted our mission to “promote the open development of artificial general intelligence through the Whole-Brain Architecture approach” in the summer of 2023, emphasizing that AGI to be promoted for development is brain-morphic.
Given the current situation in which rapid advances in AI technology are increasing risks, including human survival, our activities to maintain the technical conditions necessary for the construction of highly interpretable human brain-morphic AGI have the potential to contribute to the reduction of such risks. We sincerely appreciate your understanding and continued support in this regard.

 Japanese
Japanese