Our Policy for FY 2016
Towards WBA co-production infrastructure
Looking Back: the Initial Policy
WBAI had the following objectives at its inauguration in August 2015.
- Sustainability: retaining its objectives towards an expected advent of AGI (beyond 2030).
- Publicness: publishing research results and developing software with an open license.
- Cooperation with academia: promoting interactions among academic areas such as neuroscience, cognitive science and machine learning, with AI as the pivotal area.
- Human resource development: fostering multi-domain knowledge required for WBAI research.
- Infrastructure research: creating platforms for machine learners, evaluation methods for AGI, and research environments for simulation and data preparation.
- Social activity: making advanced AI technologies transparent for the public to create the future with AI.
Through discussions, it has been made clear that WBAI should encourage researches by the WBA approach rather than doing research itself. It is to avoid rivaling with other research entities and to be consistent with our policy for open technology.
Major recent trends with regard to policy making for FY 2016
The following are three major trends with regard to policy making after our inauguration.
-
- Technological acceleration: AI researches accelerate along with the advancement of deep learning. DL has been applied not only to image processing, but also to motion control and multi-modal information processing as well as to the domains of creativity and language understanding. This trend calls for short-term acceleration of technological development as well as long-term human resource development.
- Increase in AI investment in Japan: Following suite of MITI, MEXT and MIC started AI investments while those by enterprises and universities increase. This makes AI researchers and engineers quite busy for making relatively short-term results.
- The advent of OpenAI: the NPO was founded in December 2015 to promote open AI development with initial investment up to US$1 billion in commitments. It furthers the situation where AI technologies get more open and accessible.
Our Policy for FY 2016
As AI booms and investment surges in sectors such as enterprises, universities, and research institutes, AI-related organizations emerge in Japan as well. It is our pleasure to see the expansion of AI businesses including those carried out by companies supporting us. Meanwhile, AI researchers are under extreme pressure to work on short-term issues rather than to commit on long-term objectives such as realizing human-like AGI.
One of our initial objectives at inauguration was the sustainability of research. However, watching the recent technological advancement, we realized that we could not just assume that the advent of AGI would be in the remote future. Now we should reckon it as a realistic future and go forward by gathering forces in a new form.
Here, we confirm that we promote R&D towards the creation of human-like AGI through the WBA approach in order to realize the world with AI in accord with the humankind. In this regard, we decided, upon our public nature as an NPO, to invest our resources mainly in the following areas for FY 2016, while keeping our interest in the brain.
- Areas not to be bound to specific organizations or interest groups
- Areas not expected to yield short-term business successes
- Areas difficult to obtain public research funding
- Areas requiring quick and flexible responses
- Areas with possible application of neuroscientific knowledge
Thus, the role of WBAI will be to promote R&D to realize AGI referring to the brain, mainly with the collaboration of researchers. At WBAI, some of the regular members are researchers conversant with the advancement of the AI field to be ‘good ear and eye’ for timely decisions required in its role.
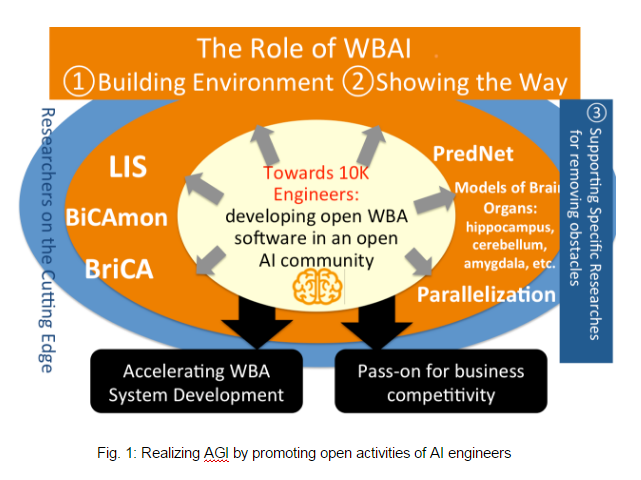
On the one hand, domestic AI researchers have less time for long-term goals, as research investments are concentrated on few of them. On the other hand, engineers are more likely to enjoy machine learning technologies that are getting more and more open. Thus, we intend to create a co-productive platform, with the idea that if WBAI prepare adequate a development environment and point to a direction, some of IT engineers (e.g., about 800K in Japan) can voluntarily get involved in the R&D of AGI (Fig. 1). In this scheme, quick and open development of WBA systems will be democratically carried out by engineers as many as 10K people, by their co-production with a shared plan of the brain provided from WBAI.
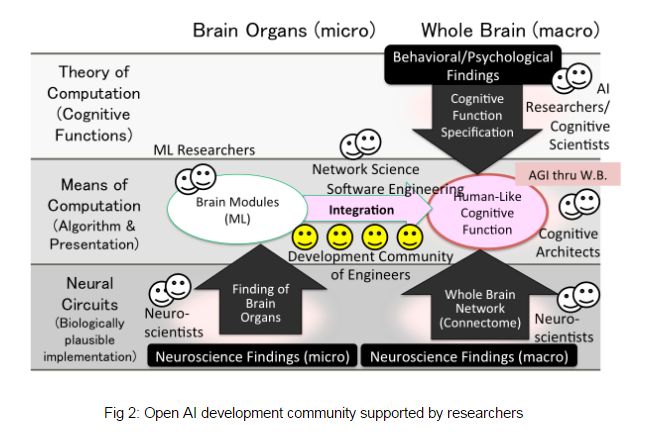
In the WBA approach, we believe co-productive development of WBA by a community will be an important option for hastening the reach to AGI (Fig. 2). With the central hypothesis of WBA, development in a community becomes possible by decomposing the entire R&D into the R&D of brain modules and that of brain-like cognitive architecture. To support this development, micro and macro level neuroscientific knowledge is required. Knowledge in AI and cognitive sciences is also required for the construction for cognitive architecture.
Forming an Open AI Development Community (Fig. 3 α)
With regard to the acceleration of technology, we set out for forming an open AI R&D community as large as having the population of 10K people to promote rather short-term R&D. The aim here is to expand faster open AI R&D by combining engineers and experts across the boundary of institutions. We have already formed a SIG where hackathons with activities around Deep Predictive Network and LIS (Life in Silico) the learning environment simulator for AI. By this means, AGI development from the WBA approach will be accelerated and the shared knowledge could be passed on to the organizations affiliated to the participants for the source of competitiveness.
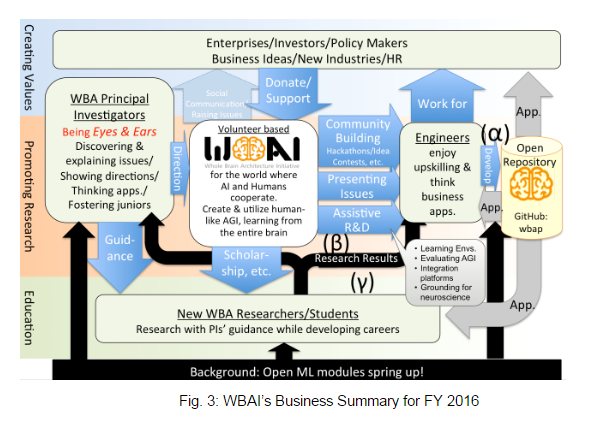
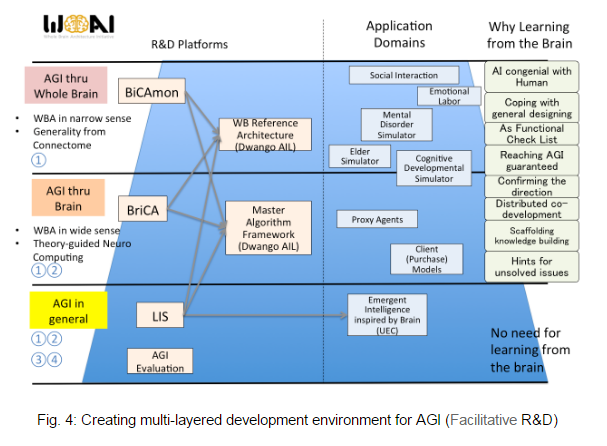
Facilitative R&D(Fig. 3 β・Fig. 4)
WBAI carries out various R&D. We continue developing BriCA, the Brain-inspired Computing Architecture, as a technology for massive distributed processing in brain-like architecture. It also develops BiCAmon, the tool for monitoring cognitive architecture’s activity while mapping it onto connectome, and LIS(Life in Silico: framework that makes intelligent agents live and learn in a virtual environment). The results have been used in the open development community as well as public and private research projects. We expect that these tools will be useful in areas where brain-like AI are applied.
Supporting Specific Researches (Fig 3 γ)
Though various machine learning techniques are getting open, it requires knowledge and skills to integrate them into WBA. As this task is generally not so easy for engineers interested in AI, it would be valuable to have support from researchers by, for example, breaking down the construction of the entire architecture into development themes.
Instead of employing PIs (principal investigators), we are going to financially support researchers who recently started to work on the WBA approach.
Summary for FY 2016 Business
In FY 2016, we shall be mainly engaged in the support of specific researches with PIs, entry level researchers and students (Fig. 3 γ), an open AI community activity centered around engineers (Fig. 3 α), and facilitative R&D lead by WBAI (Fig. 3 β), to accumulate R&D result in an open repository, so that we could pass it generally on to the society as well as to our stakeholders.

 Japanese
Japanese